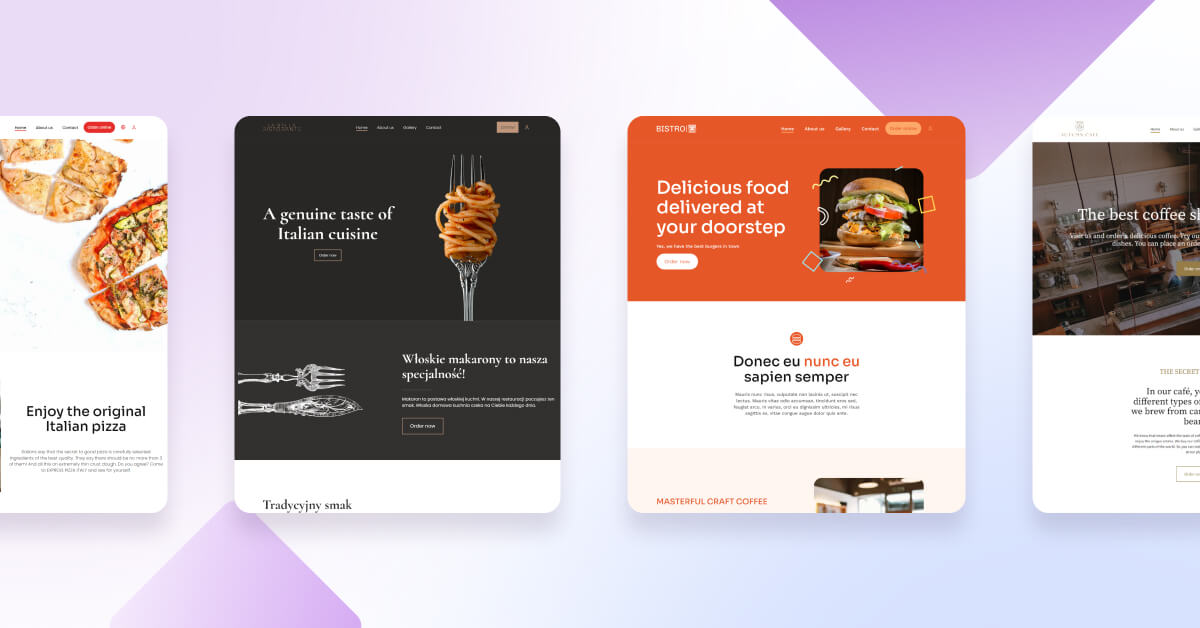
A restaurant menu is a powerful sales tool that directly impacts your restaurant’s profitability. Whether referring to a printed menu or an online menu, it plays a key role in influencing a customer’s decision to order from your restaurant.
With over six years of experience working with restaurants, I know how a well-crafted menu can boost sales and increase the average check. It’s more than just a list of dishes; it’s one of your most effective marketing tools.
When guests are deciding whether to dine in or order online, they care most about the food and prices. American diners come to the restaurant prepared, 83% check the menu in advance, and 50% decide what to order before they arrive.
To help you design a menu that attracts customers and drives results, I’ve prepared this practical guide on how to create a restaurant menu. Here’s how to craft a menu that can boost your restaurant’s financial performance.
Key Takeaways
- Treat Your Menu as a Sales Tool: A thoughtfully designed menu isn’t just informational, it’s persuasive. 48% of guests say the menu selection influences their decision to try a new restaurant.
- Limit Menu Choices to Guide Decisions: 79% of Americans struggle to decide what to order. Aim for around seven items per category, keeping your restaurant menu to a total of 30–40 items. Remember that seven is the sweet spot, and fewer than 10 items per section provides variety without overwhelming guests.
- Use the Golden Triangle Rule: Customers’ eyes naturally follow a pattern known as the Golden Triangle, starting in the middle, then moving to the top right and top left of the menu. Position high-margin items in these hot spots to increase visibility and boost sales.
- Use Descriptive Names & Images to Drive Orders: Adding enticing, descriptive names to menu items can boost sales by up to 28%, and pairing them with high-quality photos further enhances their appeal.
- Price Tactically to Increase Sales: Use pricing techniques like charm pricing (e.g., $9.95 instead of $10) and price anchoring (placing premium items near mid-range options) to subtly influence customer decisions. These strategies increase perceived value and can help raise your average check without significantly increasing restaurant costs.
- Design with Readability and Branding in Mind: Use 2–3 brand-aligned colors, simple fonts, and high-contrast combinations to ensure readability. Premium paper or laminated menus enhance durability and reinforce quality, which are key elements of strong restaurant branding.
- Check the Menu Before Printing: Always review for typos, pricing errors, and layout issues, as even small mistakes can damage credibility and incur costs.
- Prioritize Your Online Menu: Your online menu is just as important as the printed one. Use professional menu templates from an online menu creator to achieve a consistent, mobile-friendly layout, and include high-quality photos to enhance the digital ordering experience.
- Use QR Codes for Easy Access: Create a QR code menu to provide guests with instant access to your menu on their phones, enhancing convenience for both dine-in and takeout options.
- Review and Update Regularly: Analyze sales data each season to identify top performers and underperformers. Ongoing menu engineering helps improve profit margins and keep your offerings fresh.
How to Make a Restaurant Menu
Creating a restaurant menu design involves arranging dishes in a way that encourages customers to order. Well-crafted custom menus can boost sales, especially when offered in both print and digital formats.
Digital menus can increase restaurant revenue by 25–30%, but when paired with high-quality food imagery, that increase can soar to as much as 65%.
To reach more customers and drive orders, ensure you create both a printed menu and a digital restaurant menu.
Remember that building a profitable menu requires the right format, structure, pricing, and design. Below, I’ve outlined 11 actionable steps to help you get started.
Step 1. Choose the Types of Menus Your Restaurant Will Offer
The very first step is to decide what types of menu you will offer. Below, I’ve listed some of the most common menu formats restaurants use, each designed to serve different customer needs and business goals.
- À la carte – Items are priced individually, allowing customers to build their own meal.
- Prix fixe menu – A set menu with a fixed price, often featuring multiple courses and limited options.
- Digital / QR code menu – Accessible via smartphone, this modern format saves printing costs and allows for quick updates.
- Seasonal / rotating – Menus that change regularly based on ingredient availability or special themes.
- Takeout-only – A simplified version of your menu optimized for delivery and takeaway orders.
- Brunch / lunch-only menus – Limited-time menus offered during specific hours to target midday or weekend crowds.
Step 2. Create a List of All Menu Items
Once you know what type of menu (or menus, for example, if you plan to offer separate breakfast, lunch, or takeout menus) you want to create, the next step is to prepare a detailed list of the menu items you plan to offer.
Then, you can build a restaurant menu in Excel or Google Sheets, or even use a piece of paper to list all menu items.
When creating restaurant menus, remember to include the following:
- Names of dishes
- Descriptions of dishes
- Menu items prices
- List of ingredients used to prepare a dish
- Information on allergens
Remember that a well-structured menu is about making it easy for customers to understand what they’re ordering. Clear, concise, and informative menus lead to faster decisions and better dining experiences.
Too many choices can overwhelm customers and reduce sales, a concept known as the paradox of choice. In a well-known study by Iyengar and Lepper, people were 10x more likely to buy when offered fewer options.
Step 3. Decide on Menu Categories
The next step is to create restaurant menu categories. These could include, for example, breakfast, starters, soups, main courses, and drinks.
Once your categories are set, consider which menu items you want to promote most. For example, which high-margin main dish should appear at the top of the list, and why?
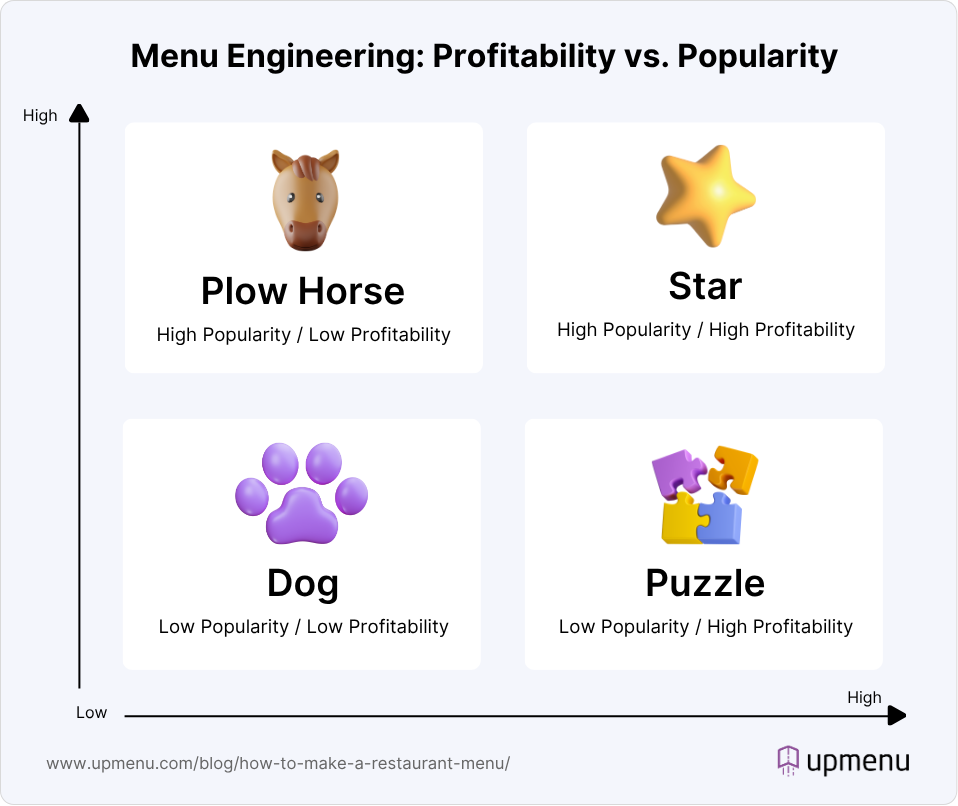
A recognizable method of grouping menu items into four categories based on their profitability and popularity is a key part of the menu engineering process. These categories include “plow horses”, “stars”, “dogs”, and “puzzles”, which represent your menu items.
Most restaurant menus work best with 5–7 main categories, striking a balance between clarity and variety. This range keeps the menus user-friendly without overwhelming customers.
A study in the Journal of Culinary Science & Technology supports this, showing that diners prefer 6 items per category for quick service and 7–10 for fine dining. Keeping your menu simple and organized helps guide decisions and boost sales.
Step 4. Price Menu Items
Once you have organized your menu items into categories using menu engineering principles, it’s time to focus on your restaurant menu pricing.
- Research the Market: Analyze competitor pricing, location, and customer demographics.
- Calculate Costs: Factor in ingredients, restaurant labor costs, and overhead to determine food cost percentage.
- Use Pricing Strategies: Employ techniques such as anchoring and odd pricing to influence the perception of value. For example, pricing a premium item higher than others can make other items seem more reasonably priced.
- Test and Adjust: Use a soft opening or focus group, then refine prices based on sales and customer feedback.
- Stay Competitive: Keep up with market trends and regularly review your pricing.
Alternatively, analyze your sales reports if you are already running a restaurant and want to increase menu prices.
A good practice for increasing menu prices is to inform customers about the changes made as a result of this rise. For example, you can put a note, “Thanks to the price increase, we can rely on fresh ingredients when cooking for you, despite the high price increase due to inflation”.
Experts, including restaurant consultants, recommend around 7 items per category, totaling about 35 items, to offer enough variety without overwhelming customers.
Step 5. Write Menu Descriptions
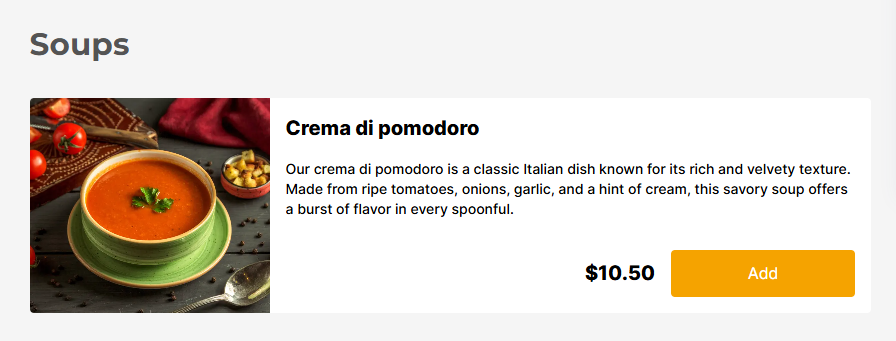
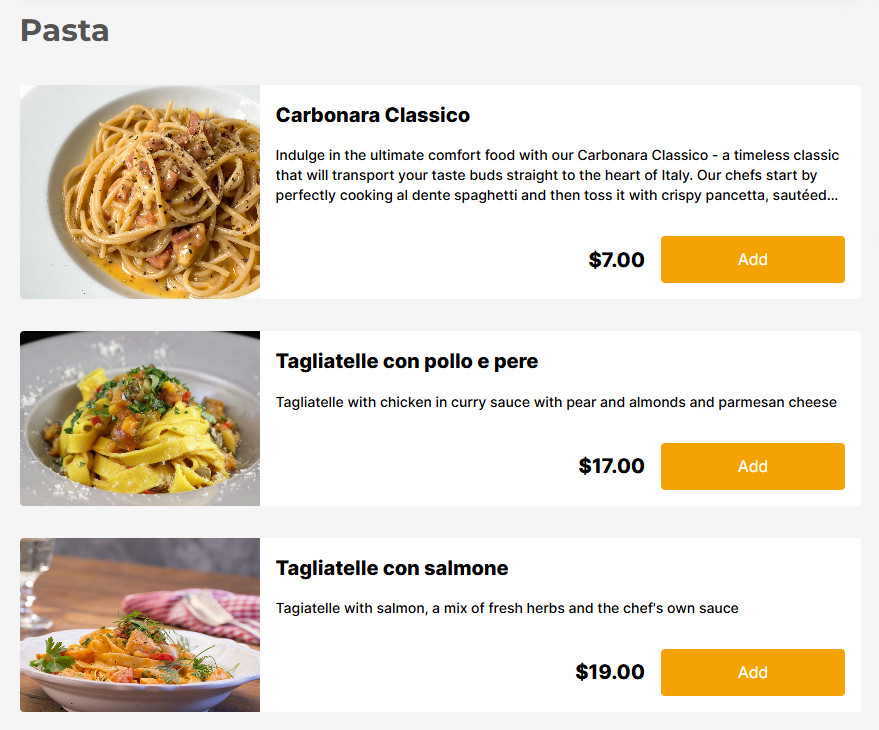
The next step is to create menu descriptions for your dishes. Discuss the ingredients used in each dish with your chef and consider why these items are included on your menu to write compelling descriptions that highlight flavor, quality, and purpose.
- Use Expressive Language (Without Overdoing It): Add vivid adjectives to highlight flavors and ingredients, but avoid exaggeration.
- Keep It Short: Descriptions should be clear, concise, and easy to read.
- Highlight Key Ingredients: Focus on what makes the dish unique or special.
- Mention Presentation: Use words that reflect how the dish looks on the plate.
- Tell a Story: Share a brief origin, chef’s inspiration, or preparation detail.
- Note Dietary Info: Indicate if a dish is gluten-free, vegan, etc.
- Avoid Clichés: Skip overused terms like “mouthwatering” and use fresh, authentic language instead.
A study by the Cornell Food and Brand Lab found that consumers are 27% more likely to choose a menu item with a descriptive name over a standard one.
That’s why, for example, instead of listing an item as “Grilled Chicken”, renaming it “Herb-Marinated Grilled Chicken Breast with Roasted Garlic Aioli” can make it sound more appealing and increase the chances a customer will order it.
You can also use a simple name and then provide a vivid description underneath to enhance its appeal without overwhelming the menu. For example, list the item as “Grilled Chicken” and follow it with a description like “Juicy, herb-marinated chicken breast served with roasted garlic aioli and seasonal vegetables.”
Step 6. Choose a Color Scheme
Selecting the right colors for your restaurant menu can reveal a great deal about your brand, so making thoughtful choices is crucial.
The colors of your restaurant menu should be consistent with your restaurant branding and interior design. Moreover, the colors you pick can influence your guests’ hunger levels.
- Red: Stimulates appetite and enhances recognition.
- Yellow: Evokes freshness and stimulates appetite.
- Green: Represents health and freshness, ideal for plant-based dishes.
- Blue: Creates a calm and relaxed atmosphere, ideal for upscale dining.
- Orange: Stimulates appetite and symbolizes nutrition.
- Brown: Conveys warmth and comfort, great for traditional or home-style cooking.
- Black: Implies sophistication and luxury, perfect for upscale restaurants.
To choose the right colors, consider using free color palette tools that help you create balanced, visually appealing combinations. Tools like Coolors, Adobe Color, and Canva Color Palette Generator can help you explore different palettes that align with your restaurant’s concept.
Step 7. Design and Optimize Your Restaurant Menu Layout
Now it’s time to design your restaurant’s menu. You have two options: use menu design tools available on the market, or hire a professional designer. If you decide to do it yourself, check out some restaurant menu design ideas for inspiration.
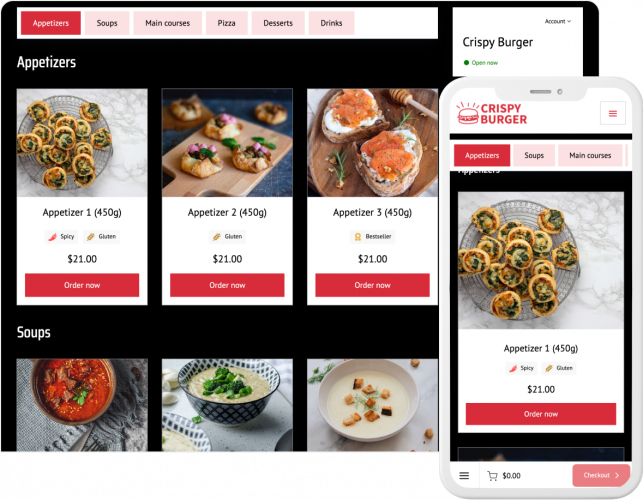
When creating an online version of your menu, consider using ready-made menu templates. Usually, you can customize these templates to create a beautifully designed menu that captures attention and helps boost orders for your restaurant.
While designing your menu, don’t forget to follow these basic best practices:
- Golden Triangle: Place high-margin items where the eye naturally goes first.
- Keep Menu Short: Create a concise menu to avoid overwhelming guests.
- No Currency Symbols: Remove symbols like $ to reduce price sensitivity.
- Avoid Price Columns: Prevent price-based decisions by integrating prices into descriptions.
- Use a Clear Structure: Organize items logically for easy readability.
Here is a menu engineering guide where you can read more about these rules.
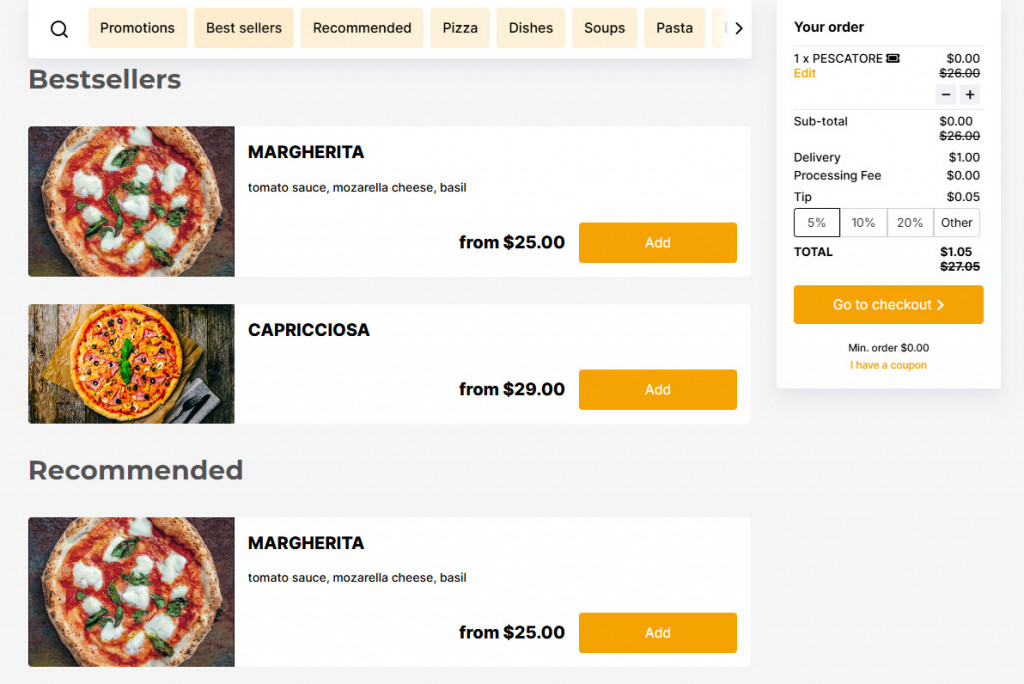
Step 8. Include High-Quality Restaurant Menu Photos
When designing a printed menu, maintain a balance. Ample white space makes the menu visually appealing, while overloading it with photos or icons can distract from the main content.
If adding images, ensure they are high-quality—blurry photos can deter customers. Focus on featuring pictures of your most popular or high-value items to draw attention and boost sales.
Remember to add your high-quality pictures to your restaurant’s online menu as well. In UpMenu restaurant menu maker, you can simply do this by clicking the upload icon on the left side of your menu item and adding a product image.
Here is a list of food photography tips to help make your restaurant’s dishes more tempting and attractive to your customers.
Alternatively, you can hire a professional photographer, but you must face additional costs in this case.
Step 9. Define Fonts, Layout, and Brand Style
Now that you’ve created a list of menu items, organized them into sections, and selected your color scheme and photos, it’s time to decide on the fonts, spacing, and overall layout of your menu.
You can do this yourself, for example, by using a free menu maker (check out this list of menu making apps I tested), or hire a professional to help you design a polished food menu.
- Use Easy-to-Read Fonts: Select clear, legible fonts such as Arial, Helvetica, or Verdana for improved readability.
- Limit Font Choices: Stick to one or two fonts to keep the menu clean and organized.
- Match Your Brand: Select fonts that reflect your restaurant’s brand and style.
- Consider Menu Item Descriptions Length: Adjust the font size based on the length of your menu descriptions.
- Use Font Variations for Emphasis: Highlight specials or signature items with bold, italics, or size changes.
Pay attention to overall menu composition, use consistent spacing, balanced margins, and precise alignment to improve readability. A well-composed layout looks professional and subtly influences ordering behavior.
Regularly updating your menu should be simple and help keep things fresh and exciting for your customers.
Step 10. Choose the Final Menu Format and Layout
After following the previous steps, you’ll have a few design options to choose from. Pick the custom menu design that best reflects your restaurant’s concept and appeals to your customers.
Consult with your staff or friends to gather feedback before making a final decision.
Step 11. Review and Print Your Menu
Before printing your restaurant menu, carefully proofread it to ensure that spelling, grammar, formatting, and consistency are accurate. Typos or layout issues can make a bad impression, so consider asking a colleague or friend to review it as well.
Once everything is checked, you’re ready to print your menu. Be sure to choose the right size and paper quality. The paper should be durable and of high quality, with a weight that suits your menu’s format and design.
When selecting the size, take into account:
- Font size
- Number of menu items
- Overall layout and spacing
- Standard (8.5″ x 11″): The most popular size for dine-in restaurants. Easy to read and ideal for menus with many items.
- Compact (5.5″ x 8.5″): Common in cafes and diners. A budget-friendly option for smaller menus.
- Large (11″ x 17″): Used in upscale restaurants or as inserts for specials. Offers more space for design and larger fonts.
- A4 (8.27″ x 11.69″): Widely used outside the U.S., especially in Europe, Asia, and Australia.
- Custom sizes: Tailored to fit specific branding or layout needs. Ideal for restaurants with unique design preferences.
Build and Optimize Your Online Restaurant Menu
Now that you’ve created and printed your restaurant menu, it’s time to set up an online menu.
When creating your online restaurant menu, make sure it’s easy to navigate, mobile-friendly, and optimized for fast loading to enhance the customer experience.
Below, I’ve outlined the key tips on how to make a restaurant menu online.
1. Use UpMenu to Create Your Digital Menu
When you create a digital menu with UpMenu, it works just like a restaurant website. This means you can:
- Use it as a standalone solution
- Install it on your existing website
- Build a new restaurant website using the UpMenu restaurant website builder
If you choose to create a restaurant website using the builder, select a menu template and customize it to match your brand and menu offerings.
Check out this guide to learn more about the steps on how to create a restaurant website.
You can design custom menus with menu making apps. Just choose a free online menu maker, select from available free menu templates, and customize it with your restaurant’s branding, colors, fonts, and photos.
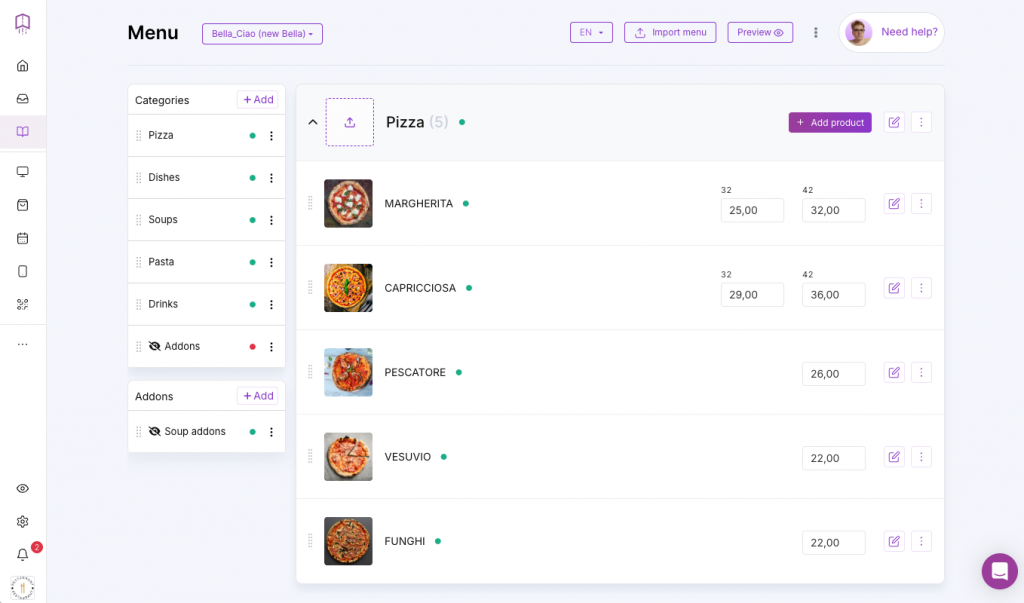
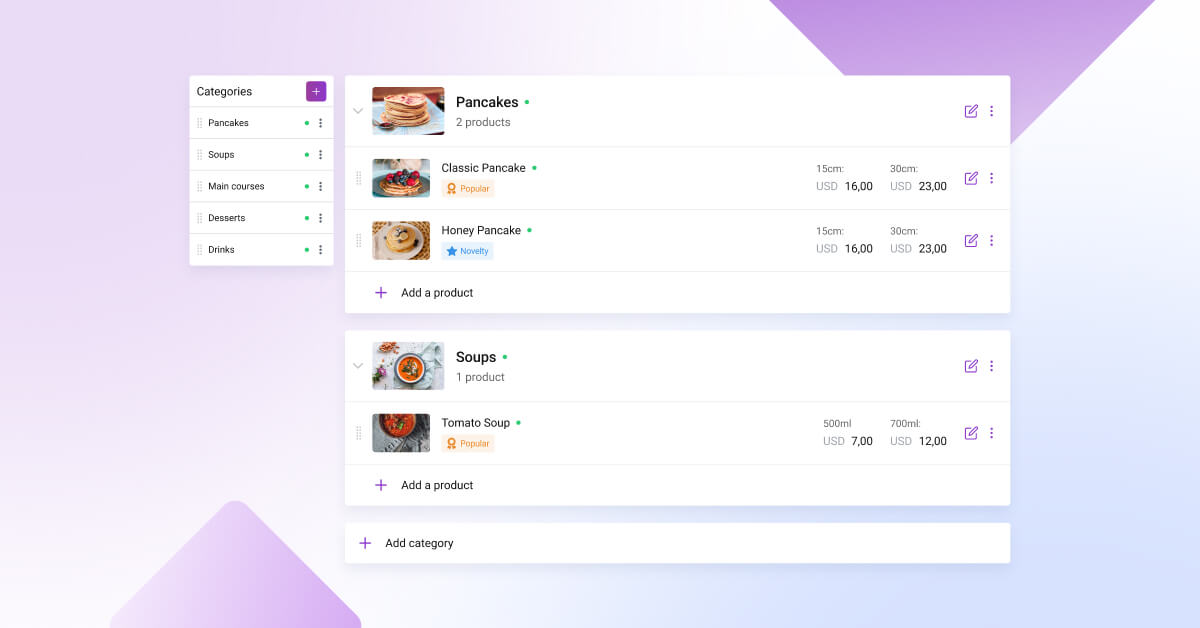
2. Add Menu Categories and Items
Once you have selected and customized your menu template, start creating menu categories and adding menu items from your printed menu.
Enter each item on your menu, along with its name, description, and price.
3. Reuse Descriptions and Photos from Your Printed Menu
Remember that you can add the same menu item descriptions and photos as you used for your printed menu.
Bear in mind that you’ll need high-quality photos of your dishes. Take clear, well-lit photos of each item on your menu.
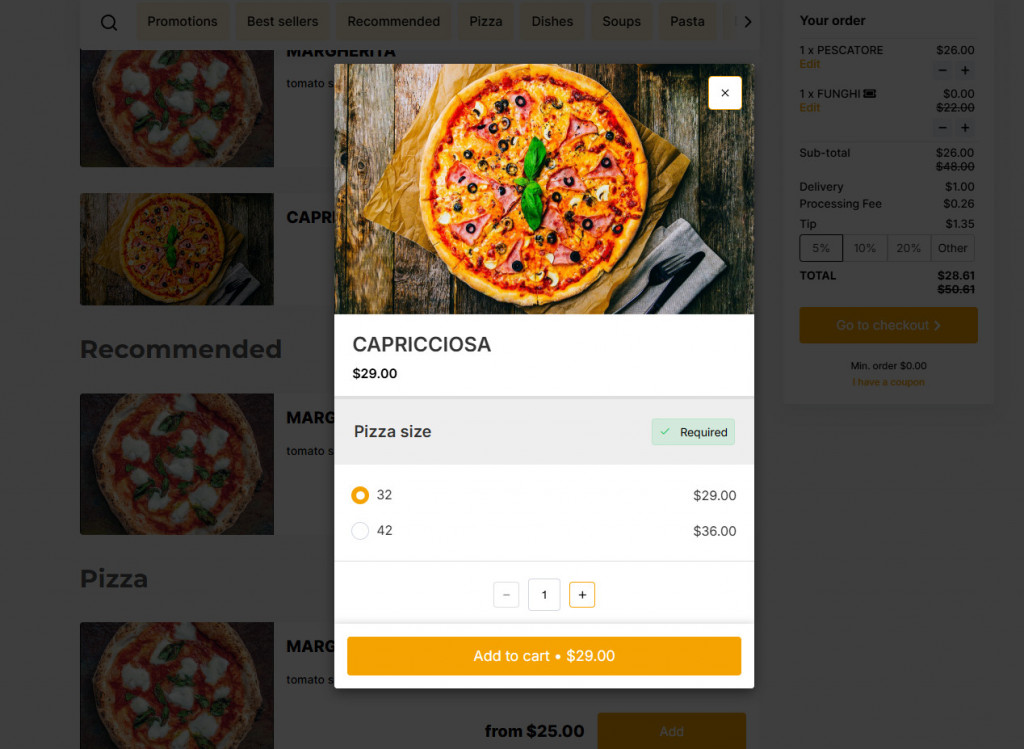
4. Add Modifiers for Customization
Let guests personalize their dishes by selecting portion sizes, choosing free or paid extras, or swapping ingredients.
Menu item modifiers are a valuable feature of menu management software, allowing restaurants to offer additional ingredients, substitutions, or upgrades.
This feature also enables flexible pricing based on portion size or selected add-ons, giving customers more choice while increasing order value and average check.
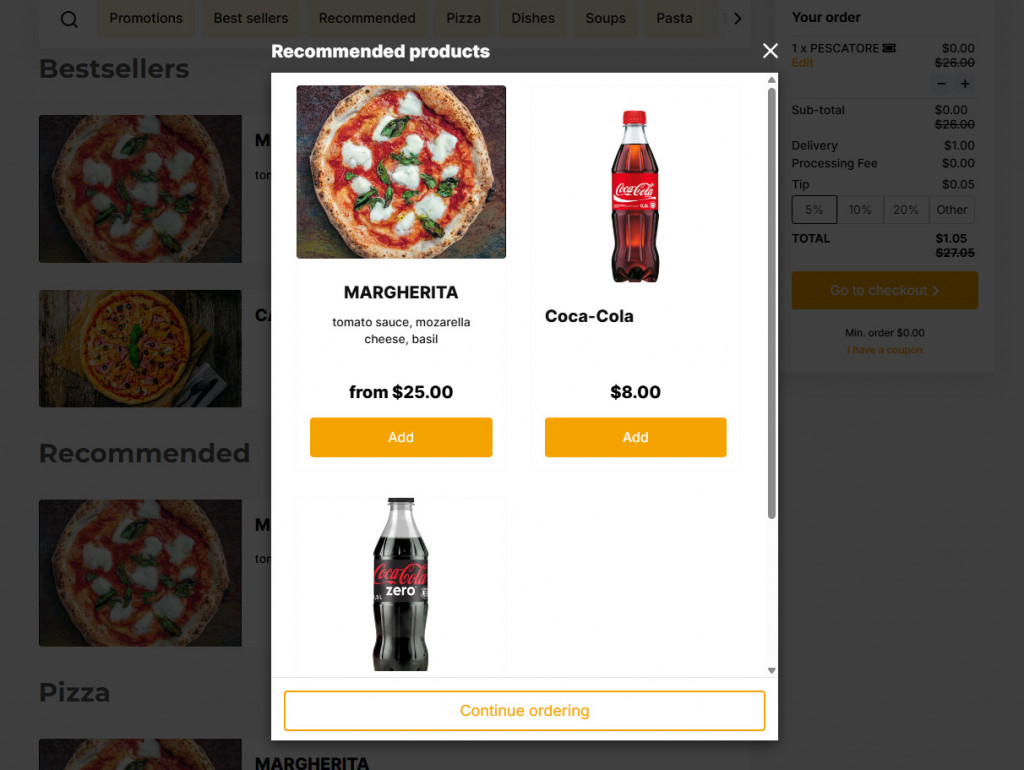
5. Use Upselling Recommendations
Increase sales by suggesting bestsellers or recommended items directly on the menu. Utilize methods such as highlighting popular dishes or displaying a pop-up with add-ons before checkout.
Restaurants using UpMenu often begin with customizable menu templates for both their website and mobile app. With built-in upselling tools, 51% report higher order values, and over 40% of total revenue comes from mobile app orders, proving that a well-designed digital menu is key to boosting sales.
Upselling not only boosts the average restaurant revenue but also enhances the customer experience by guiding them toward popular or complementary choices. Most online menu tools offer built-in upselling features to simplify this process.
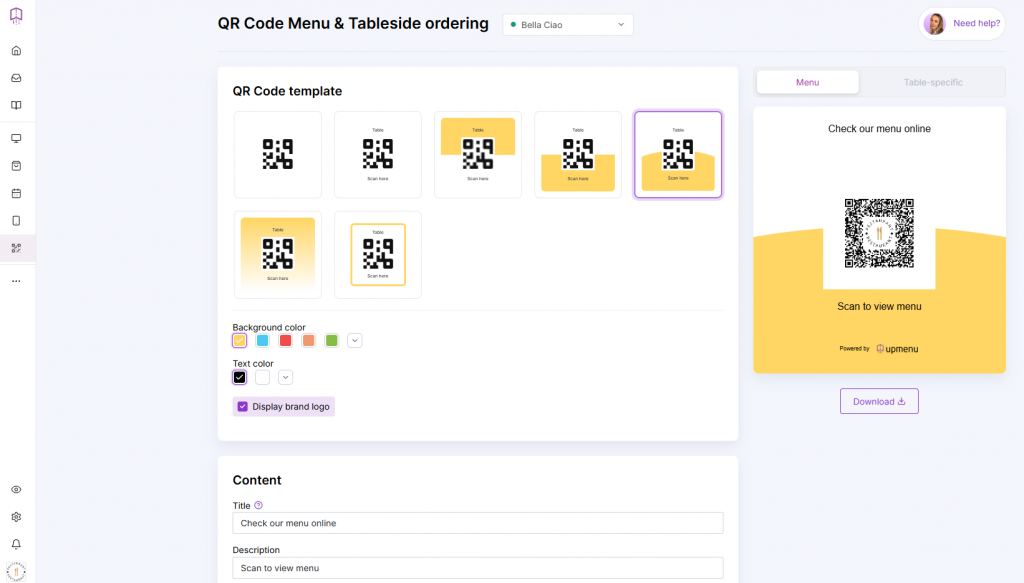
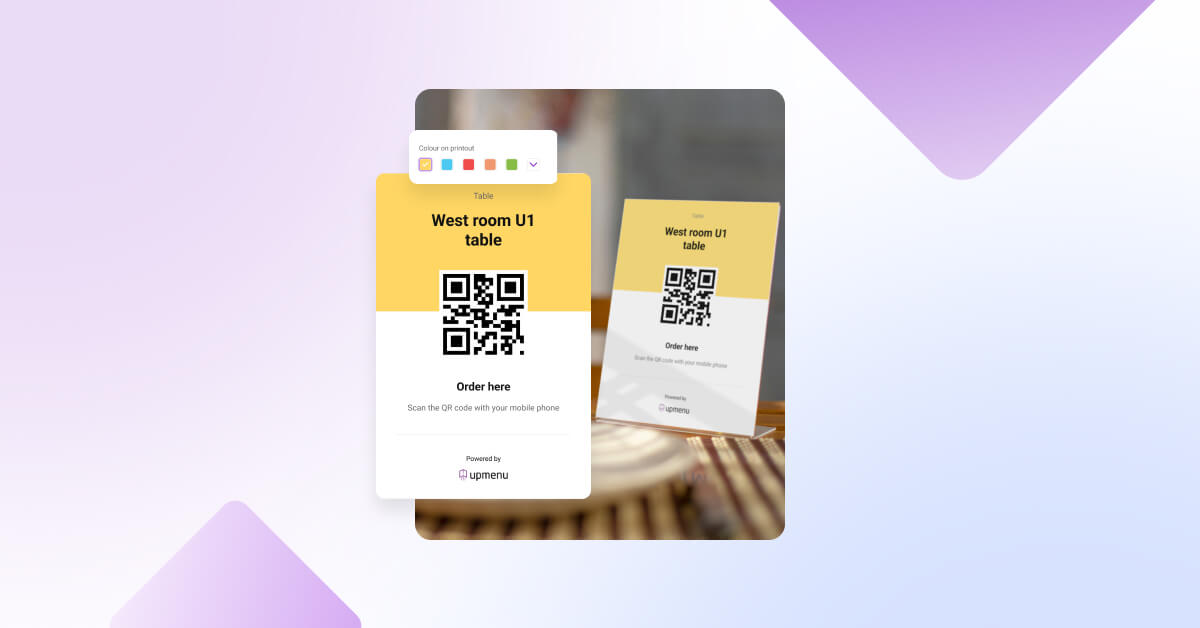
6. Create a QR Code Menu for Easy Access
Create a QR code menu to let guests scan and access your digital menu anytime, which is perfect for dine-in, takeout, or restaurant promotions.
Restaurants using UpMenu’s QR code menu see a 17% boost in online orders and a 23% increase in table turnover, thanks to real-time updates and faster service.
7. Enable Tableside Ordering
Don’t forget about tableside ordering. This option allows clients to order their meals directly from the table, making it convenient for both you and your customers.
8. Update and Optimize Continuously
Utilize restaurant analytics to monitor customer behavior and menu performance, then refine your online menu in real-time for improved results.
Regularly updating your menu helps highlight top-selling items, remove underperformers, and test new dishes. This ongoing optimization can lead to increased sales and a more positive customer experience.